 Decreased genetic correlation of recombination landscapes with increased genetic distance
Decreased genetic correlation of recombination landscapes with increased genetic distanceAbstract
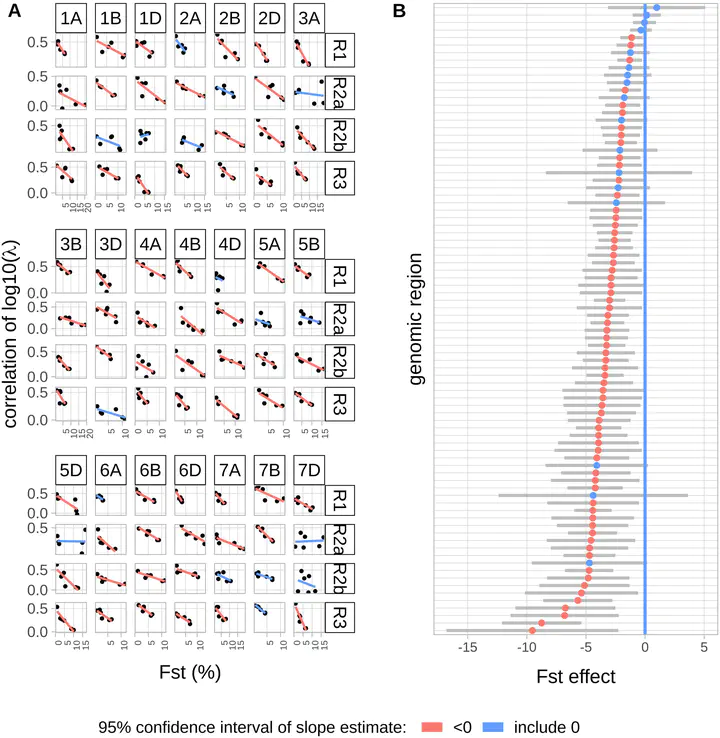
Reciprocal exchanges of DNA (crossovers) that occur during meiosis are mandatory to ensure the production of fertile gametes in sexually reproducing species. They also contribute to shuffle parental alleles into new combinations thereby fueling genetic variation and evolution. However, due to biological constraints, the recombination landscape is highly heterogeneous along the genome which limits the range of allelic combinations and the adaptability of populations. An approach to better understand the constraints on the recombination process is to study how it evolved in the past. In this work, we tackled this question by constructing recombination profiles in four diverging bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) populations established from 371 landraces genotyped at 200,062 SNPs. We used linkage disequilibrium (LD) patterns to estimate in each population the past distribution of recombination along the genome and characterize its fine-scale heterogeneity. At the megabase scale, recombination rates derived from LD patterns were consistent with family-based estimates obtained from a population of 406 recombinant inbred lines. Among the four populations, recombination landscapes were positively correlated between each other and shared a statistically significant proportion of highly recombinant intervals. However, this comparison also highlighted that the similarity in recombination landscapes between populations was significantly decreasing with their genetic differentiation in most regions of the genome. This observation was found to be robust to SNPs ascertainment and demography and suggests a relatively rapid evolution of factors determining the fine-scale localization of recombination in bread wheat.